When an area of the brain is in use blood flow to that region also increases. Single-cell recordings primarily measure the brains A.
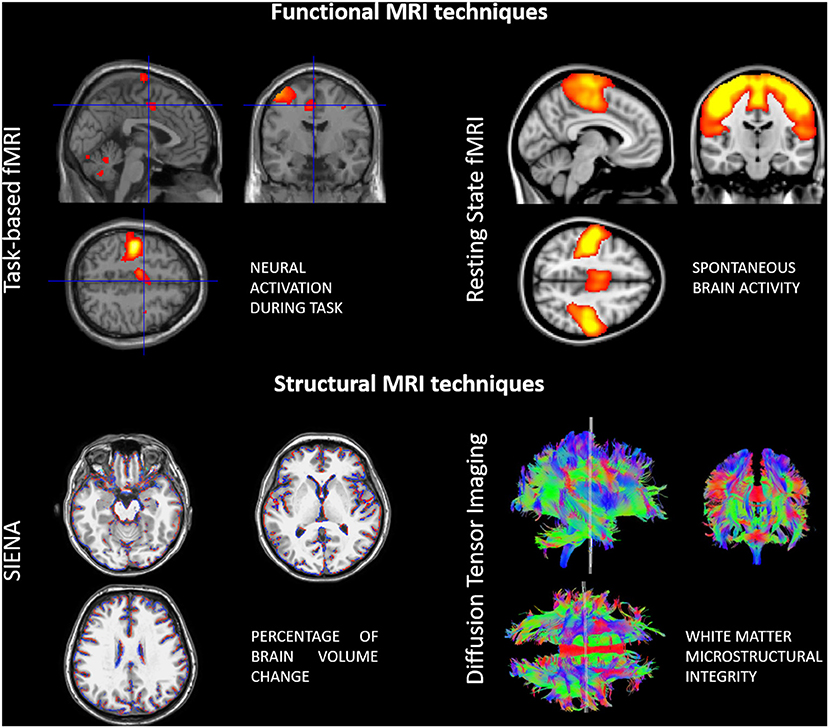
Frontiers Neuroplasticity And Motor Rehabilitation In Multiple Sclerosis A Systematic Review On Mri Markers Of Functional And Structural Changes Neuroscience
As a noninvasive imaging modality able to show the dynamic changes in neurologic activity functional magnetic resonance imaging has revolutionized the ability to both map and further understand the functional regions of the brain.

. Functional magnetic resonance imaging fMRI relies on the paramagnetic properties of oxygenated and deoxygenated haemoglobin to see images of changing blood flow in the brain associated with neural activity. Ultimately because feasible fMRI techniques all depend on the neurovascular response still deeper understanding will be needed of the geometry of the cortical and subcortical microvasculature the molecular signals relating neural electrical activity to vasodilation and vasoconstriction the spatial distribution of pericytes the details of oxygen extraction and the. This allows images to be generated that reflect which brain structures are activated and how during performance of different tasks.
Functional MRI has grown from the conjunction of two phenomena. Functional magnetic resonance imaging fMRI is a neuroimaging technique gaining greater momentum and use by professionals since its invention in 1990. The fMRI adaptation technique is making use of the reduced signal which accompanies repeated presentations of the same or related stimuli with a signal rebound observed when an unrelated stimulus is subsequently presented Grill-Spector and Malach 2001.
MRI The signal measured in a PET scan is generated by radioactive decay. This method is thus relying on a repetition-related memory. For example the widely available scanning technique visualizes activity in all areas of the brain not just those close to the surface.
Functional magnetic resonance imaging or functional MRI fMRI measures brain activity by detecting changes associated with blood flow. Functional magnetic resonance imaging fMRI is a technique for measuring and mapping brain activity that is noninvasive and safe. The brainthe last frontier of modern science.
The biophysical effect that deoxyhemoglobin has magnetic properties that affect the MR signal and the physiological effect that CBF increases much more than oxygen metabolism as neural activity changes so that the deoxyhemoglobin level changes as neural activity changes. FMRI can measure brain activity without opening the skull or exposing the brain cells to harmful. Hemoglobin molecules also carry iron and therefore have a magnetic signal.
Functional Magnetic Resonance Imaging fMRI refers to the use of the technology of magnetic resonance imaging MRI to detect the localized changes in blood flow and blood oxygenation that occur in the brain in response to neural activity. Hyder and Rothman 2012. It is being used in many studies to better understand how the healthy brain works and in a growing number of studies it is being applied to understand how that normal function is disrupted in disease.
Despite many technological advances we still know little about how the brain works. A In the control state the arterial supply is. In addition to the above a few radical fMRI approaches have tried to resolve endogenous activity-dependent brain signals arising from non-hemodynamic sources such as diffusion changes Le Bihan 2007 neuronal magnetic fields Bandettini et al 2005 and metabolite-dependent spectroscopic signals Mangia et al 2009.
Naccache and Dehaene 2001. Luckily the development of a technique called functional magnetic resonance imaging fMRI is slowly helping change this. Functional magnetic resonance imaging measures activity-dependent changes in blood oxygenation.
This technique relies on the fact that cerebral blood flow and neuronal activation are coupled. Current applications range from neurosurgical planning to an enormous variety of investigational applications across many diverse specialties. The fMRI technique makes use of activity-dependent changes in.
The fMRI technique makes use of activity-dependent changes in. Unlike PET it does not rely on radiation or a radiolabeled tracer. The magnetic field from the MRI interacts with the protons in our hydrogen atoms 3 its of course pretty handy that we are 70 water there are plenty of hydrogen.
Metabolic activity Oxygen exchange OD. The fMRI technique makes use of activity dependent changes in blood oxygen levels Electroencephalography measures changes in voltage generated by large groups of neurons What imaging technique has the highest spatial resolution. Today not only have researchers used this.
A new technique called molecular fMRI has the potential to help bridge this divide. Blood flowing through the brain carries oxygen on molecules called hemoglobin. Molecular fMRI is an alternative form of fMRI that monitors brain activity through the use of chemical or genetically-encoded probes designed to sense specific molecular and.
When an area of the brain is in use blood flow to that region also increases. Single-cell recordings primarily measure the brains A. This technique relies on the fact that cerebral blood flow and neuronal activation are coupled.
The fMRI technique which emerged in the early 1990s offered significant advances over other methods of studying brain function. Functional magnetic resonance imaging or functional MRI fMRI is an MRI procedure that measures brain activity by detecting associated changes in blood flow. Question 5 2 2 pts The fMRI technique makes use of activity-dependent changes in.
The Blood Oxygen Level Dependent BOLD Response - the basis of fMRI - Relative levels of deoxyhaemoglobin change from regional cortical activity - Momentary decrease in blood oxygenation immediately after neural activity increases known as the initial dip in the haemodynamic response function HRF. Functional MRI makes use of a special signal called blood oxygen level-dependent BOLD contrast. As the name suggests magnets are central to magnetic resonance imaging but quite a bit stronger roughly 1000 to 3000 times stronger than the average fridge magnet.
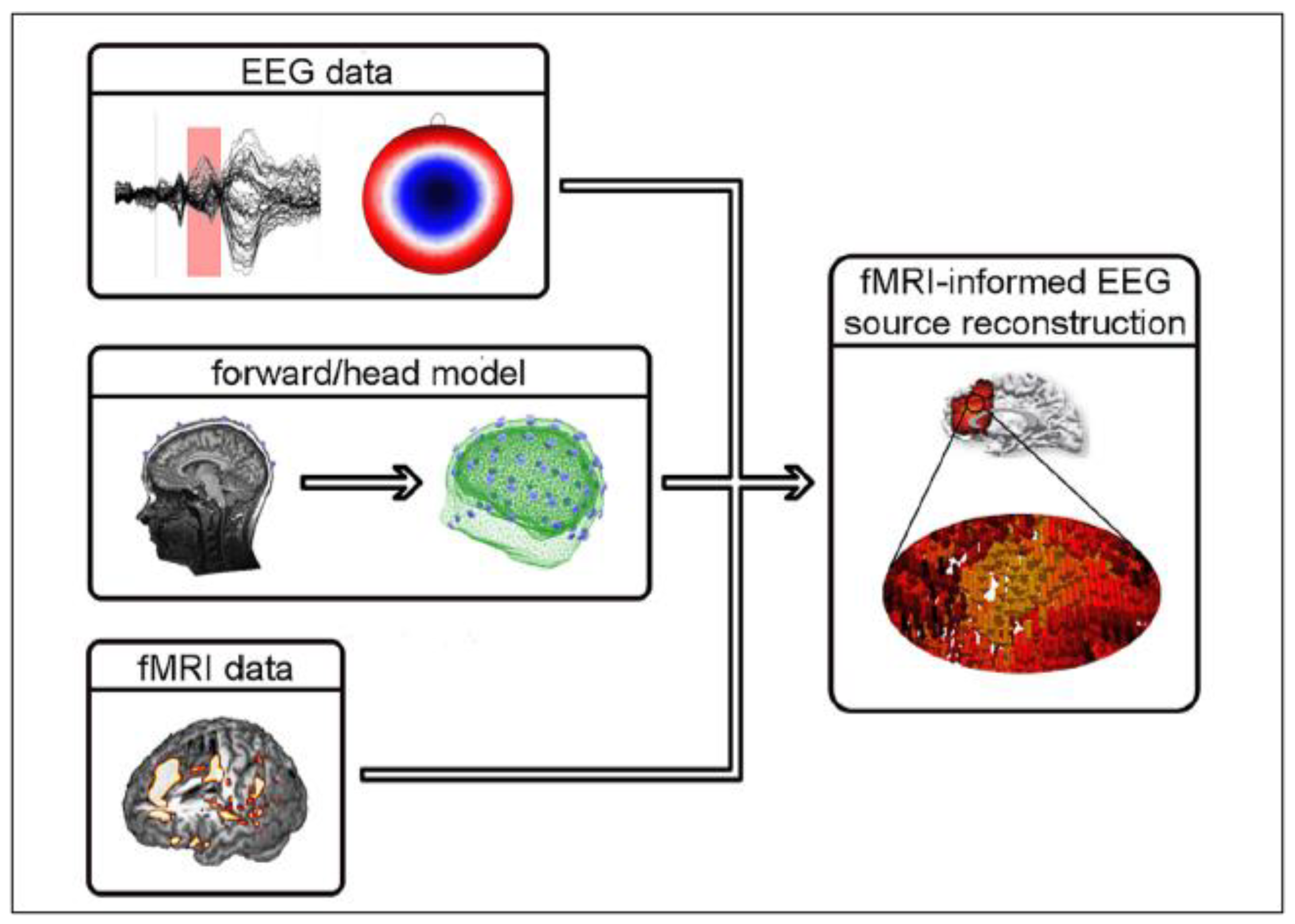
Sensors Free Full Text Simultaneous Eeg Fmri What Have We Learned And What Does The Future Hold Html

Eeg Vs Mri Vs Fmri What Are The Differences
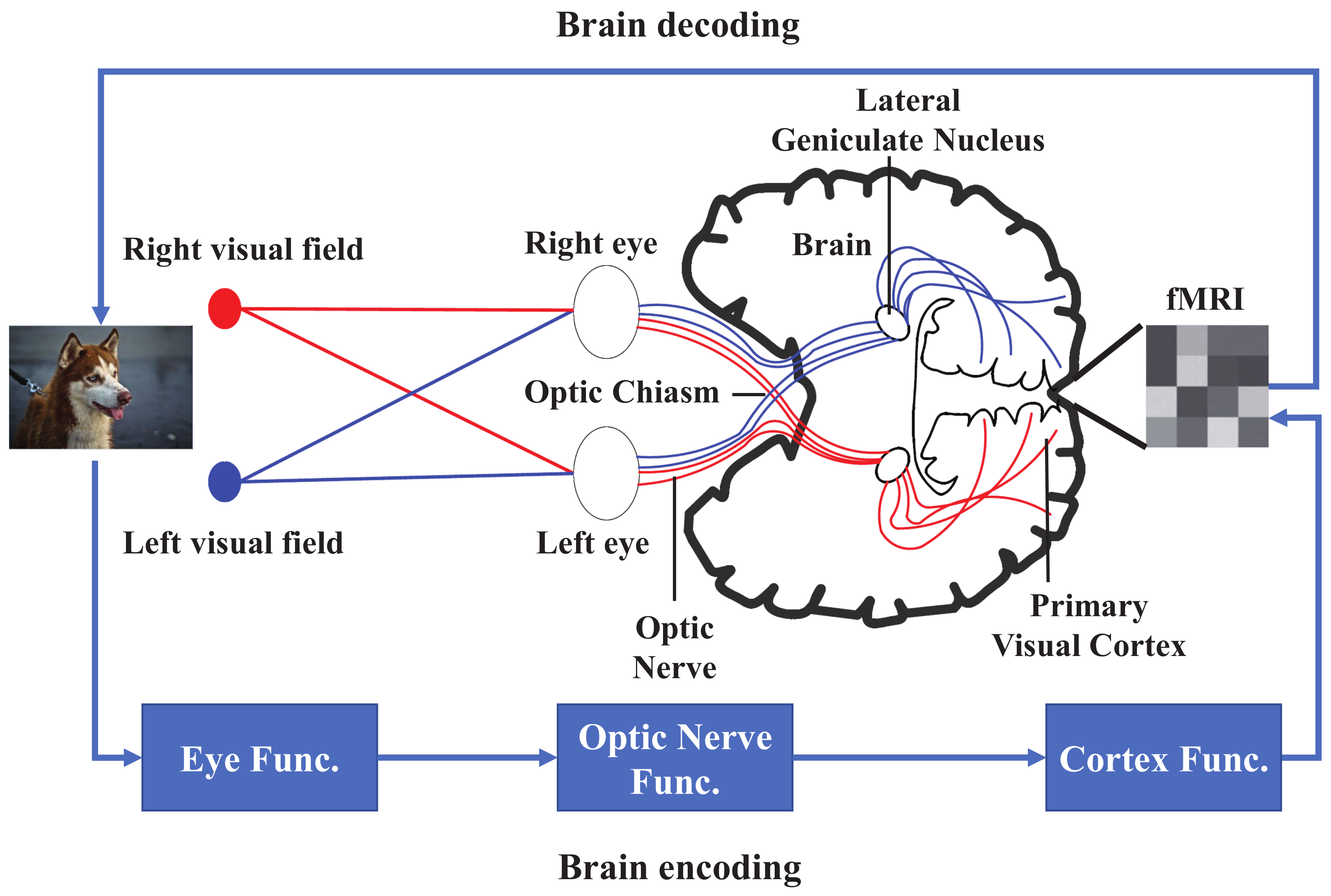
Brain Sciences Free Full Text Fmri Brain Decoding And Its Applications In Brain Ndash Computer Interface A Survey Html
0 Comments